What is an Automotive PCB?

PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is the abbreviation for printed circuit board, serving as the carrier of electronic components and an essential part of electronic devices. An automotive PCB is a PCB specifically designed for automotive electronic systems, meeting the high standards and strict requirements of the automotive industry, such as high temperature, high humidity, high vibration, and high reliability. Depending on the size and complexity of the circuit board, automotive PCBs can be in the form of single-layer, double-layer, multi-layer, rigid, or flexible boards.
Differences Between Automotive PCBs and Standard PCBs
- Material Selection There are differences in material selection between automotive PCBs and standard PCBs. Standard PCBs typically use FR-4 fiberglass material, while automotive PCBs use composite materials, which are prefabricated materials composed of two or more materials. These materials not only meet the requirements for use in high-temperature, high-humidity environments but also effectively reduce noise and interference in the vehicle’s circuits.
- Process Requirements The process requirements for automotive PCBs are more stringent than those for standard PCBs. Due to the harsh working environments and vibration impacts that automotive PCBs must endure, higher process standards are needed. For instance, automotive PCBs require more rigorous soldering and protective treatments to ensure circuit stability and reliability. Additionally, automotive PCBs must meet higher fire resistance and corrosion protection standards, particularly following the automotive industry standard IATF16949.
- Environmental Adaptability Standard PCBs are primarily used in general electronic devices with relatively low environmental requirements. In contrast, automotive PCBs must adapt to more complex automotive working environments, such as high and low temperatures, humidity, and vibration. Therefore, automotive PCBs must have superior heat resistance, humidity tolerance, and vibration resistance.
- Reliability The reliability requirements for automotive PCBs are significantly higher than those for standard PCBs. Since automotive PCBs play critical roles in automotive electronic systems, they must have enhanced aging resistance, corrosion resistance, and interference resistance. They also need to undergo rigorous reliability testing to ensure stability and reliability under various extreme conditions.
- Thickness Requirements Automotive PCBs have stricter thickness requirements. Standard PCBs generally have a thickness of 0.2-3.0mm, while automotive PCBs typically range from 0.6-3.2mm. This increased thickness is necessary because automotive electronic components operate in harsher environments, requiring PCBs to be more durable and stable.
Applications of Automotive PCBs
Automotive PCBs are widely used in automotive electronics, in-car audio systems, in-car multimedia, and navigation systems. They not only enhance the safety and reliability of automotive circuits but also improve operational efficiency and performance. The key application areas of automotive PCBs include:
- Safety Systems Used in airbags, anti-lock braking systems, vehicle stability control systems, parking sensors, and blind-spot monitoring to enhance driving safety.
- Infotainment Systems Applied in dashboards, navigation systems, audio systems, in-car telephony, and connected car systems to increase driving comfort and enjoyment.
- Powertrain Systems Employed in engines, transmissions, battery management, chargers, and motor control systems to improve driving performance and energy efficiency.
- Sensor Systems Utilized in temperature sensors, pressure sensors, flow sensors, oxygen sensors, and humidity sensors to improve driving accuracy and intelligence.

Market Outlook and Development Trends of Automotive PCBs
With the advancement of smart and electrification trends, the number of automotive electronic devices is steadily increasing, leading to an expanding automotive PCB market. In the future, as 5G and IoT intelligent technologies develop, automotive electrification will deepen, providing broader prospects for the automotive PCB market.
The development of new energy vehicles and autonomous driving technologies also offers more opportunities for the automotive PCB market. As the electrification of new energy vehicles intensifies, the demand for automotive PCBs will continue to grow. Meanwhile, the application of autonomous driving technologies will lead to a significant increase in the number of in-car and external connected devices, further boosting the automotive PCB market.
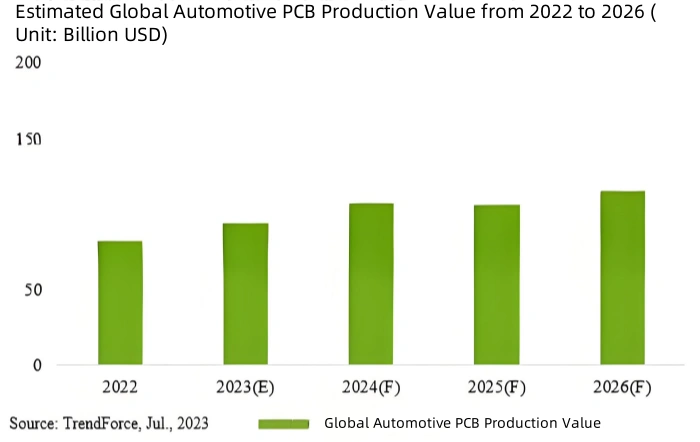
According to the “Global Automotive PCB Market Outlook” report by TrendForce, due to the high proportion of PCB applications in consumer electronics, the impact of economic headwinds on the PCB industry is more significant than on other components, given the lack of a clear recovery in end-market demand. The global PCB market is estimated to be worth approximately $79 billion in 2023, a decline of 5.2% from 2022. However, the automotive PCB market is expected to grow against this trend, primarily driven by the continuous rise in global electric vehicle penetration and automotive electronics. The automotive PCB market is projected to grow by 14% in 2023, reaching $10.5 billion, with its share of the total PCB market rising from 11% in 2022 to 13%. By 2026, the automotive PCB market is expected to reach $14.5 billion, accounting for 15% of the total PCB market, with a CAGR of approximately 12% from 2022 to 2026.
Conclusion
In summary, there are significant differences between automotive PCBs and standard PCBs in material selection, process requirements, environmental adaptability, and reliability. As automotive electronics technology continues to advance, the demand for automotive PCBs will continue to grow, with increasingly stringent requirements for quality and reliability. In the future, developing and producing high-quality automotive PCBs will be crucial for driving the growth of the automotive electronics industry.
Related Posts
PCBA Prototype
December 14, 2025
PCB Assembly
September 2, 2025