Introduction to PCB: Types, Applications and Manufacturing Services

In the complex world of modern electronic devices, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the unsung heroes. They’re like the infrastructure of a city, silently supporting the smooth operation of electronics by providing electrical connections and physical support for various components. From everyday items like smartphones and computers to industrial automation equipment and medical instruments, PCBs are everywhere. Their unique structure and functions ensure the miniaturization, high performance, and reliability of electronic devices. Simply put, without PCBs, the development of modern electronics would be impossible.
Understanding PCBs: The Basics
What is a PCB?
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a key electronic component that connects various electronic parts through conductive pathways on an insulating substrate. Think of it as the “nervous system” of an electronic device, linking components together so current can flow along designated paths to perform functions like signal transmission and power distribution. Its working principle is based on Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Law, which guide the flow of electricity through connected components to complete the circuit and enable the device to perform complex tasks. For example, in a smartphone, the PCB connects components like the processor, memory, and camera, allowing them to work together for functions like calls, photos, and web browsing.
Structure and Components of a PCB
A typical PCB consists of several parts:
- Insulating Substrate: This is the base of the PCB, often made from materials like fiberglass or epoxy resin, providing mechanical strength and excellent insulation to support the electronic components.
- Conductive Tracks: Copper is commonly used for the conductive pathways that transmit current and signals.
- Pads: The pads are the areas where electronic component leads are soldered to connect with the conductive tracks.
- Vias: These are holes that connect different layers of a multi-layer PCB, ensuring signals can travel between them.
- Soldermask: A protective layer (often green) covering the PCB to prevent short circuits during soldering and protect the copper tracks from oxidation.
Different Types of PCBs
Single-Layer PCB: Simple Yet Effective
A single-layer PCB is like a straightforward one-lane street, with all the circuits and components laid out on just one layer. Its simple structure makes it easy to design and manufacture, which keeps costs low. This type of PCB is often used in basic electronic devices like calculators, simple radios, or LED lights, where the circuits don’t need to be overly complex.
Double-Layer PCB: A Smart Solution
A double-layer PCB has conductive pathways on both sides of the board, similar to a two-way street that provides more space for the circuit layout. The circuits are connected through vias, which allow the board to handle more complex circuits while maintaining a compact size. This type of PCB is commonly used in devices like smartphones and motherboards, where space is at a premium but more advanced functionality is needed.
Multi-Layer PCB: Mastering Complexity
A multi-layer PCB consists of several double-layer boards stacked together, like a multi-story building, with each layer providing additional circuits. These PCBs are ideal for high-performance devices like servers, graphics cards, and aerospace equipment, where multiple layers help with signal isolation and managing more complex circuits.
Flexible PCB: The Art of Flexibility
A flexible PCB is made from bendable materials like polyimide, allowing it to be folded, bent, or rolled up. This flexibility enables better use of space in devices that need to fit into tight or curved areas. Common applications include wearables, smartphone camera modules, and laptop display connectors.
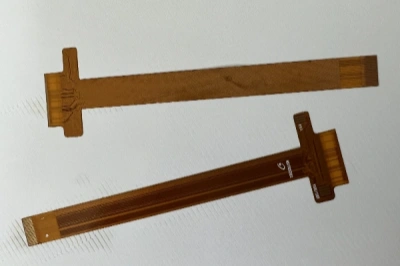
Rigid-Flex PCB: A Powerful Combination
A rigid-flex PCB combines the benefits of both rigid and flexible PCBs. It uses flexible layers for wiring and rigid layers for component mounting. This hybrid solution is ideal for applications like aerospace, medical devices, and automotive electronics, where space and reliability are crucial.

High-Frequency PCB: Speeding Up Signal Transmission
A high-frequency PCB is designed to transmit signals above 1 GHz, like a race car speeding down a highway. These PCBs are used in telecommunications, radar, and satellite systems where fast and stable signal transmission is critical.

Aluminum-Based PCB: Heat Dissipation Expert
An aluminum-backed PCB uses aluminum as the base material, offering excellent heat dissipation. It helps electronics stay cool, particularly in applications like LED lighting and power electronics, where overheating can lead to failure. Aluminum PCBs are cost-effective, lightweight, and environmentally friendly.
PCB Applications Across Industries
Consumer Electronics: Lighting Up Every Moment
In consumer electronics, PCBs are at the core of every device. In smartphones, they connect the processor, memory, camera, and communication modules, allowing for seamless operation. As smartphones become slimmer and more powerful, the demand for multi-layer PCBs and HDI (High-Density Interconnect) PCBs grows to accommodate more complex circuits in compact spaces.
In computers, the motherboard—a multi-layer PCB—integrates components like the CPU, GPU, memory, and storage, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Other devices like graphics cards and sound cards also rely on PCBs to connect with the motherboard, adding extra functionality.
Automotive Electronics: Driving Future Mobility
In the automotive industry, PCBs are crucial for the smart and electric vehicles of tomorrow. They are used in engine control systems, airbag modules, and in-car entertainment systems. In electric vehicles, PCBs connect sensors and control units, optimizing vehicle performance and safety.
Medical Equipment: Protecting Life’s Health
In the medical field, PCBs play a vital role in MRI machines, pacemakers, and blood pressure monitors. They provide the necessary electrical connections and support, ensuring devices function accurately and safely, which is critical for patient health.
Industrial Control: The Brain of Smart Factories
In industrial automation, PCBs are the “brains” of systems like PLCs and DCS. They connect various components and manage data to ensure smooth and efficient manufacturing processes. Industrial robots, powered by PCBs, help automate tasks like welding, assembly, and packaging, improving productivity and precision.
Telecommunications: Connecting the World
In telecommunications, PCBs are essential for transmitting signals in 5G base stations, routers, and switches. They ensure high-speed, stable data transfer, which is vital for global communication.
Conclusion
PCBs have evolved from simple, single-layer boards to complex, high-frequency designs that are integral to everything from consumer electronics to medical devices and automotive technologies. As technology advances, PCBs will continue to evolve, enabling even smaller, more powerful, and more efficient electronic devices. Without PCBs, the modern world of electronics simply wouldn’t function.
Trust GreatPCB to Meet All Your PCB Manufacturing Needs
Whether you need a simple single-layer PCB or a highly complex 30-layer multi-layer PCB, GreatPCB can bring your ideas to life. We offer a wide range of PCB manufacturing services, from standard fiberglass PCBs to rigid-flexible PCBs. We also provide high-frequency PCBs and aluminum-backed PCBs for unique applications.
Get Instant Quotes for FR4 PCB Manufacturing
Looking for pricing on flexible PCBs, rigid-flex PCBs, aluminum PCBs, Rogers PCBs, or other specialty PCBs? Simply reach out to us and send your Gerber files along with material and quantity requirements, and we will provide a quote promptly.
We also offer PCB prototyping services, allowing you to get the right PCB design before full production. Avoiding costly mistakes can save you thousands in project costs. All our designers comply with the ISO 9001:2008 quality management system, and our in-house quality control team will verify that your prototype meets both our and your high standards before shipping. For quick prototyping needs, most designs can be completed in just 4-5 days.
Instant Quote for Quickturn PCB Prototyping
Once your PCB is fabricated or prototyped, we also offer assembly services. Whether it’s for prototype assembly, contracted PCB assembly, turnkey PCB assembly, or partial/full assembly, we can tailor our services to meet your unique requirements. We can handle a wide range of quantities, from low-volume, high-mix assembly to mass PCB assembly. All our turnkey services are IPC Level 3 compliant and certified under ISO 9001:2008.
At GreatPCB, we handle basic PCB design tasks like surface mount or through-hole connections, as well as more challenging mixed-assembly products. As part of our quality control, we offer Design for Manufacturability (DFM) testing. Additionally, we can perform specific functional tests to ensure the PCBs we manufacture meet their design specifications.
Related Posts
PCBA Prototype
December 14, 2025
PCB Assembly
September 2, 2025