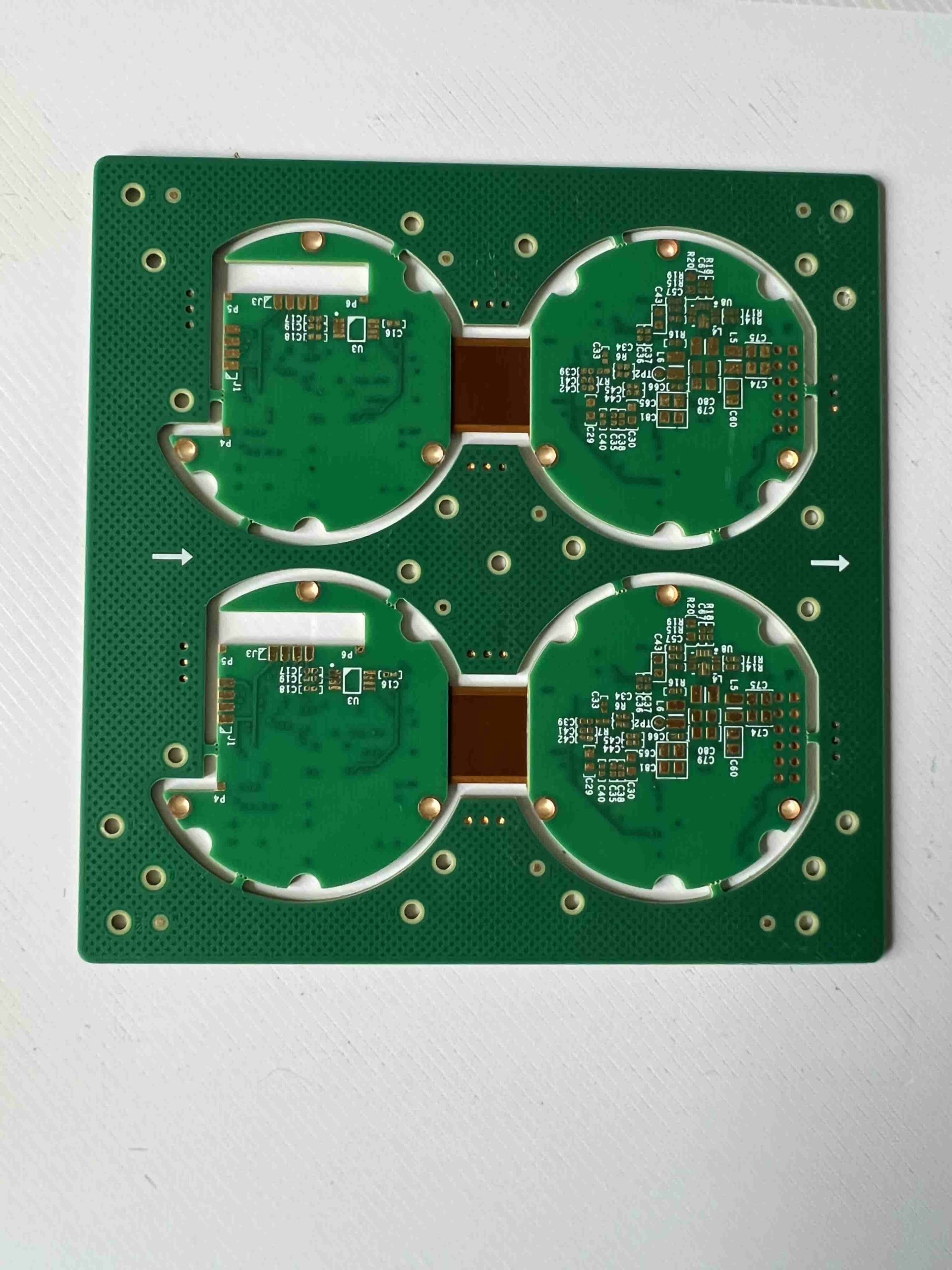
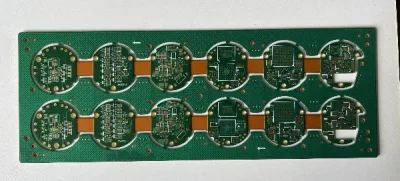
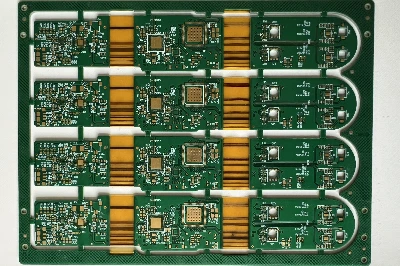
What is Rigid-Flex PCB?
Rigid-Flex PCB (Rigid-Flex Printed Circuit Board) is a type of circuit board that integrates both flexible and rigid circuit board technologies into a single structure. This design combines the stability of rigid PCBs with the flexibility of flex PCBs, allowing the board to bend in specific areas while remaining rigid in others. This unique configuration offers greater design freedom and is suitable for applications requiring complex three-dimensional routing.
Advantages of Rigid-Flex PCB
- High Space Utilization
One of the main advantages of rigid-flex PCB is its ability to maximize space utilization. Its flexible design allows the board to be folded or bent to fit within confined spaces, thus reducing the overall size of the device. - Reduction in Connectors and Fixtures
By combining flexible and rigid sections, rigid-flex PCBs can eliminate many traditional cable connections and connectors, simplifying assembly and reducing potential failure points, which enhances the product’s reliability. - Lower Assembly Costs
Since a rigid-flex PCB integrates multiple circuit boards into a single structure, it reduces the number of soldering, assembly, and testing steps, thereby lowering overall production costs.
Disadvantages of Rigid-Flex PCB
Despite its advantages, rigid-flex PCB also has some drawbacks:
- High Production Complexity
The process of combining flexible and rigid materials is more complex than manufacturing purely rigid or flexible boards. This complexity can lead to longer production times and increased costs. - High Design Requirements
Designing a rigid-flex PCB requires precise planning, especially when considering flexible section bending radii, stress concentrations, and thermal management. Poor design can lead to reduced board performance or failure.
Design Issues and Considerations for Rigid-Flex PCB
- Design Specifications and Requirements
It is essential to adhere to strict design specifications when creating a rigid-flex PCB. Ensure that the bending radius of the flexible sections meets manufacturing requirements to prevent material damage or board failure. - Stress Concentration and Thermal Management
Special attention should be paid to stress concentration issues in the design. Use appropriate transition areas and reinforcement structures in bending regions to minimize stress concentrations. Additionally, consider thermal management to ensure effective heat dissipation, preventing board failure due to overheating. - Circuit Layout and Routing
When laying out the circuit, carefully plan the routing for both rigid and flexible areas. Avoid high-frequency signals and high-power circuits in flexible sections to minimize electromagnetic interference and signal integrity issues. - Connections and Soldering Techniques
The connection and soldering techniques for rigid-flex PCBs are critical. Use suitable soldering technologies to ensure reliable connections between rigid and flexible parts. Consider potential damage to flexible sections during soldering and choose appropriate materials and processes. - Material Selection
Selecting the right materials is crucial for the performance of rigid-flex PCBs. Typically, rigid sections use traditional FR-4 materials, while flexible sections use high-performance polyimide (PI) materials or other flexible circuit board materials. Ensure material compatibility to guarantee overall board stability and reliability.
Applications of Rigid-Flex PCB
Rigid-flex PCBs find applications in various high-demand fields, including but not limited to:
- Consumer Electronics
In devices like smartphones, tablets, and wearables, rigid-flex PCBs help designers fit circuits into compact spaces while ensuring device reliability and durability. - Medical Devices
Medical equipment requires high precision and reliability. Rigid-flex PCBs offer flexible design solutions while ensuring performance and adaptability to various complex shapes and structures. - Aerospace and Defense
Rigid-flex PCBs are also widely used in aerospace and defense applications, where devices must operate under extreme conditions and require high reliability and stability.
Future Development of Rigid-Flex PCB
As electronic devices become increasingly miniaturized and complex, the demand for rigid-flex PCBs will continue to grow. With advancements in materials and manufacturing technologies, the performance of rigid-flex PCBs is expected to improve further, with costs potentially decreasing. Additionally, the rise of 5G, the Internet of Things (IoT), and wearable technology will further drive the need for rigid-flex PCBs in emerging fields.
Advantages of Rigid-Flex PCB from Greatpcb
As a leading PCB manufacturer, Greatpcb offers extensive experience in the design and production of rigid-flex PCBs. We are committed to providing high-quality, reliable rigid-flex circuit boards to meet various complex application needs. Whether designing intricate rigid PCB boards or high-requirement rigid-flex circuit boards, Greatpcb delivers customized solutions. Our strong R&D capabilities allow us to continuously innovate in PCB flex-rigid products to meet market demands.
At Greatpcb, we understand the unique requirements of each project and work closely with clients from design to final delivery, ensuring that every rigid circuit board meets stringent quality standards. Choosing Greatpcb means choosing quality and innovation.
Conclusion
Rigid-flex PCBs, with their unique design and multifunctionality, play an indispensable role in modern electronic products. Although there are challenges in production and design, the benefits of improving product performance, optimizing space utilization, and reducing assembly costs make them a preferred choice for many high-end applications. With ongoing technological advancements, the future of rigid-flex PCBs looks promising, and Greatpcb remains at the forefront, providing exceptional solutions for rigid-flex circuit boards.