PCB Design in the 5G World: Challenges and Solutions

PCB Design Requirements for 5G Applications
In 5G applications, the key PCB design requirements include high-frequency, high-speed materials, high-density interconnects (HDI), impedance matching, layer stack-up planning, signal integrity for trace spacing/holes, and updates in process technology and testing equipment.
Rising Demands with 5G Development
As 5G technology advances, so do PCB design requirements. Data transmission speeds have increased from 25Gbps to 56Gbps, meaning high-frequency, high-speed materials are essential for handling the signal transmission demands. Additionally, 5G encourages HDI technology development, requiring careful layer stack-up and trace/spacing design to ensure signal integrity and efficiency.
5G PCB Design Guidelines
When it comes to materials, 5G PCBs need to use high-frequency, high-speed materials. Companies like Nan Ya, Shengyi, and Panasonic are introducing new materials tailored to 5G requirements. Additionally, process technology and testing equipment must be upgraded, with high-precision devices and test equipment like impedance testers being critical to ensure quality and performance.
- Choose materials with low dielectric constant (Dk) to minimize signal loss.
- Use minimal solder masks as they absorb moisture, increasing circuit loss.
- Ensure smooth copper traces to reduce resistance, especially at high frequencies where current “skin depth” is shallow.
- Signal integrity in high-frequency circuits depends heavily on impedance control. Using mSAP technology helps achieve precise traces, improving impedance accuracy.

Automatic Testing for 5G PCB
PCBs for high-frequency applications must undergo automated testing processes like Optical Inspection (AOI) and Automated Test Equipment (ATE) to ensure quality and catch any errors early. This automation helps meet the global impedance control needs in 5G systems, ensuring consistent performance and high productivity.
Choosing the Right Transmission Lines
In high-frequency PCB design, choosing the right transmission lines (microstrip, stripline, or grounded coplanar waveguide) is crucial. Striplines may be preferable but are harder to manufacture, requiring close collaboration with manufacturers to minimize signal reflection and avoid issues during production.

#image_title
Challenges in 5G PCB Design
Engineers face several challenges when designing PCBs for 5G applications. The complexity of 5G devices requires HDI PCBs with finer traces, but these can lead to signal integrity issues at high speeds. Impedance irregularities are common due to trace size, width, and cross-section factors, causing signal loss, particularly with traditional etching methods. Advanced techniques like MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) also add complexity.
Thermal Management in 5G PCB Design
High-speed signals generate a lot of heat, making thermal management essential in 5G PCB design. Choosing the right substrates and materials to handle heat dissipation is critical, or issues like copper delamination and board warping may occur, affecting performance.
Differences Between 5G and 4G Communication PCBs
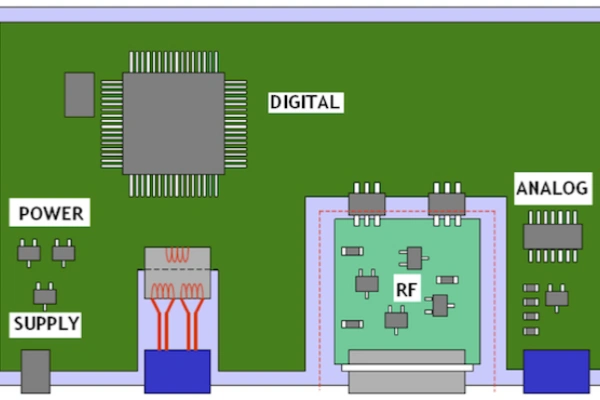
- 5G base station RF units and antennas differ significantly from 4G, especially with increased RF channels, leading to larger PCBs and greater integration.
- Millimeter wave spectrum (28G, 39G) will be widely used for high-speed transmission, increasing demand for high-frequency communication PCBs in 5G.
- High-speed copper-clad laminates will be needed for 5G equipment, including baseband units, network boards, backplanes, HDI, and high-frequency boards.
- Heat management will become even more critical with the rise of high-power density components, driving demand for advanced cooling structures and materials in future PCB designs.

#image_title
Conclusion: Evolving Design for 5G PCB Applications
PCB design for 5G involves more than just material and process updates—it requires a shift in design concepts and overcoming technical challenges to meet the performance and reliability standards expected in 5G devices.